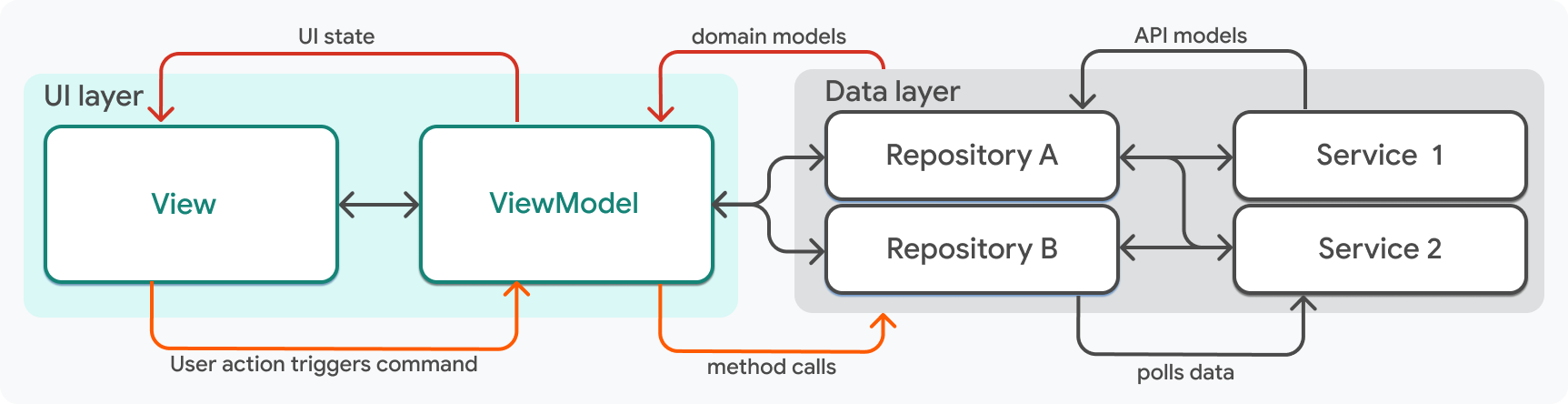
UI 層案例研究
您 Flutter 應用中每個功能的 UI 層應由兩個元件構成:一個 View 和一個 ViewModel。
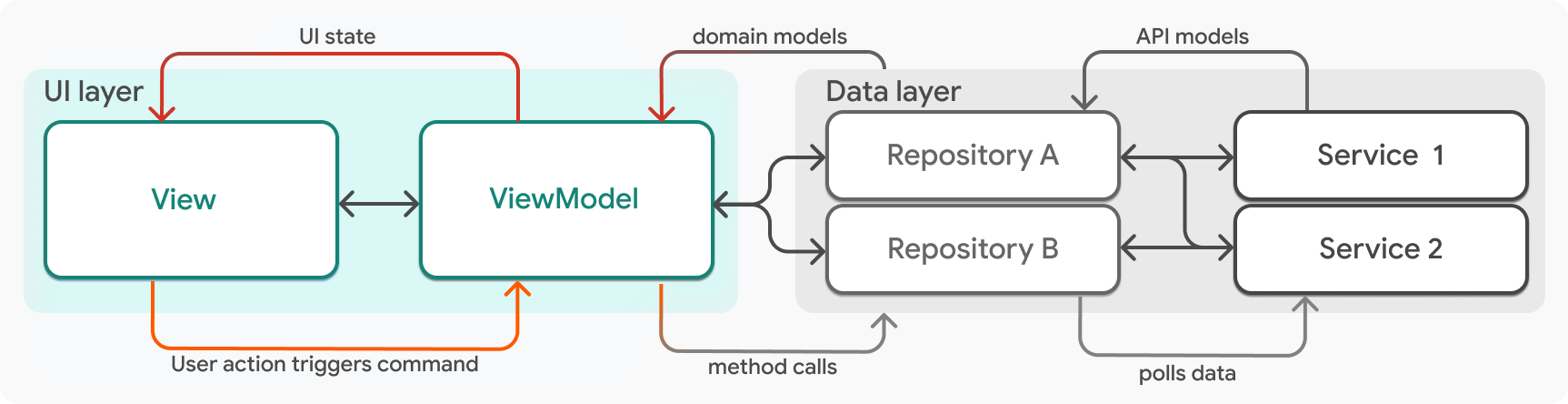
廣義上講,ViewModel 管理 UI 狀態,View 顯示 UI 狀態。View 和 ViewModel 之間存在一對一的關係;每個 View 都對應一個管理該 View 狀態的 ViewModel。每一對 View 和 ViewModel 構成一個單一功能的 UI。例如,一個應用可能包含名為 LogOutView 和 LogOutViewModel 的類。
定義 ViewModel
#ViewModel 是一個負責處理 UI 邏輯的 Dart 類。ViewModel 以領域資料模型作為輸入,並將該資料作為 UI 狀態暴露給相應的 View。它們封裝了 View 可以附加到事件處理程式(如按鈕點選)的邏輯,並負責將這些事件傳送到應用的資料層,在那裡發生資料更改。
以下程式碼片段是一個名為 HomeViewModel 的 ViewModel 類的宣告。它的輸入是提供其資料的儲存庫。在這種情況下,ViewModel 依賴於 BookingRepository 和 UserRepository 作為引數。
class HomeViewModel {
HomeViewModel({
required BookingRepository bookingRepository,
required UserRepository userRepository,
}) :
// Repositories are manually assigned because they're private members.
_bookingRepository = bookingRepository,
_userRepository = userRepository;
final BookingRepository _bookingRepository;
final UserRepository _userRepository;
// ...
}ViewModel 始終依賴於資料儲存庫,資料儲存庫作為引數傳遞給 ViewModel 的建構函式。ViewModel 和儲存庫之間存在多對多關係,大多數 ViewModel 將依賴於多個儲存庫。
如前面 HomeViewModel 示例宣告所示,儲存庫應為 ViewModel 的私有成員,否則 View 將直接訪問應用的資料層。
UI 狀態
#ViewModel 的輸出是 View 渲染所需的資料,通常稱為UI 狀態,或簡稱為狀態。UI 狀態是完全渲染 View 所需資料的不可變快照。
ViewModel 將狀態作為公共成員公開。在以下程式碼示例的 ViewModel 中,公開的資料是 User 物件,以及使用者儲存的行程,這些行程以 List<BookingSummary> 型別物件的形式公開。
class HomeViewModel {
HomeViewModel({
required BookingRepository bookingRepository,
required UserRepository userRepository,
}) : _bookingRepository = bookingRepository,
_userRepository = userRepository;
final BookingRepository _bookingRepository;
final UserRepository _userRepository;
User? _user;
User? get user => _user;
List<BookingSummary> _bookings = [];
/// Items in an [UnmodifiableListView] can't be directly modified,
/// but changes in the source list can be modified. Since _bookings
/// is private and bookings is not, the view has no way to modify the
/// list directly.
UnmodifiableListView<BookingSummary> get bookings => UnmodifiableListView(_bookings);
// ...
}如前所述,UI 狀態應為不可變的。這是無 bug 軟體的關鍵部分。
Compass 應用使用 package:freezed 來強制執行資料類的不可變性。例如,以下程式碼顯示了 User 類的定義。freezed 提供深度不可變性,並生成有用方法(如 copyWith 和 toJson)的實現。
@freezed
class User with _$User {
const factory User({
/// The user's name.
required String name,
/// The user's picture URL.
required String picture,
}) = _User;
factory User.fromJson(Map<String, Object?> json) => _$UserFromJson(json);
}更新 UI 狀態
#除了儲存狀態之外,ViewModel 還需要在資料層提供新狀態時通知 Flutter 重新渲染 View。在 Compass 應用中,ViewModel 擴充套件 ChangeNotifier 來實現此目的。
class HomeViewModel extends ChangeNotifier {
HomeViewModel({
required BookingRepository bookingRepository,
required UserRepository userRepository,
}) : _bookingRepository = bookingRepository,
_userRepository = userRepository;
final BookingRepository _bookingRepository;
final UserRepository _userRepository;
User? _user;
User? get user => _user;
List<BookingSummary> _bookings = [];
List<BookingSummary> get bookings => _bookings;
// ...
}HomeViewModel.user 是 View 依賴的公共成員。當新資料從資料層流經並需要發出新狀態時,將呼叫 notifyListeners。
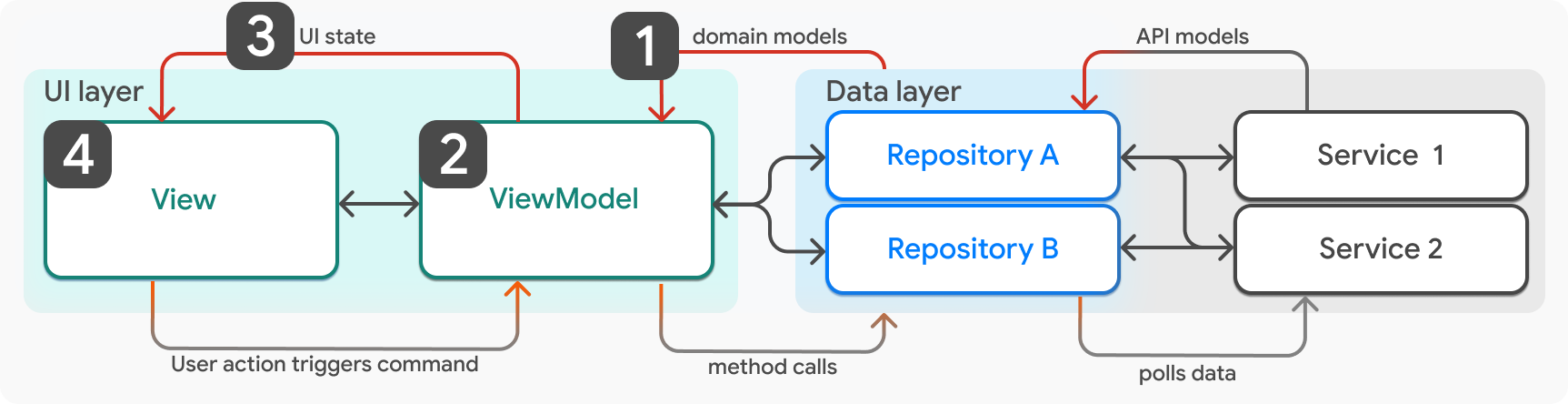
- 從儲存庫向 ViewModel 提供新狀態。
- ViewModel 更新其 UI 狀態以反映新資料。
- 呼叫
ViewModel.notifyListeners,通知 View 新的 UI 狀態。 - View (widget) 重新渲染。
例如,當用戶導航到主螢幕並建立 ViewModel 時,將呼叫 _load 方法。在此方法完成之前,UI 狀態為空,View 顯示載入指示器。當 _load 方法完成後,如果成功,ViewModel 中將有新資料,並且必須通知 View 新資料可用。
class HomeViewModel extends ChangeNotifier {
// ...
Future<Result> _load() async {
try {
final userResult = await _userRepository.getUser();
switch (userResult) {
case Ok<User>():
_user = userResult.value;
_log.fine('Loaded user');
case Error<User>():
_log.warning('Failed to load user', userResult.error);
}
// ...
return userResult;
} finally {
notifyListeners();
}
}
}定義 View
#View 是應用中的一個小部件。通常,View 代表應用中的一個螢幕,該螢幕有自己的路由,並在小部件樹的頂部包含一個 Scaffold,例如 HomeScreen,但這並非總是如此。
有時 View 是一個封裝了需要在整個應用中重用功能的單一 UI 元素。例如,Compass 應用有一個名為 LogoutButton 的 View,它可以放置在使用者期望找到登出按鈕的任何位置。LogoutButton View 有自己的 ViewModel,名為 LogoutViewModel。在較大的螢幕上,螢幕上可能存在多個 View,它們在移動裝置上會佔據整個螢幕。
View 中的小部件有三項職責:
- 它們顯示 ViewModel 中的資料屬性。
- 它們監聽來自 ViewModel 的更新,並在新資料可用時重新渲染。
- 如果適用,它們將來自 ViewModel 的回撥附加到事件處理程式。
繼續 Home 功能示例,以下程式碼顯示了 HomeScreen View 的定義。
class HomeScreen extends StatelessWidget {
const HomeScreen({super.key, required this.viewModel});
final HomeViewModel viewModel;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
// ...
);
}
}大多數情況下,View 的唯一輸入應該是 key(所有 Flutter 小部件都可以選擇性地接受它)以及 View 對應的 ViewModel。
在 View 中顯示 UI 資料
#View 依賴於 ViewModel 來獲取其狀態。在 Compass 應用中,ViewModel 作為引數傳遞到 View 的建構函式中。以下示例程式碼片段來自 HomeScreen 小部件。
class HomeScreen extends StatelessWidget {
const HomeScreen({super.key, required this.viewModel});
final HomeViewModel viewModel;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// ...
}
}在小部件內部,您可以訪問從 viewModel 傳遞過來的預訂資訊。在以下程式碼中,booking 屬性被提供給子小部件。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
// Some code was removed for brevity.
body: SafeArea(
child: ListenableBuilder(
listenable: viewModel,
builder: (context, _) {
return CustomScrollView(
slivers: [
SliverToBoxAdapter(...),
SliverList.builder(
itemCount: viewModel.bookings.length,
itemBuilder: (_, index) => _Booking(
key: ValueKey(viewModel.bookings[index].id),
booking:viewModel.bookings[index],
onTap: () => context.push(Routes.bookingWithId(
viewModel.bookings[index].id)),
onDismissed: (_) => viewModel.deleteBooking.execute(
viewModel.bookings[index].id,
),
),
),
],
);
},
),
),更新 UI
#HomeScreen 小部件使用 ListenableBuilder 小部件監聽來自 ViewModel 的更新。ListenableBuilder 小部件下的所有小部件樹都會在提供的 Listenable 更改時重新渲染。在這種情況下,提供的 Listenable 是 ViewModel。回想一下,ViewModel 的型別是 ChangeNotifier,它是 Listenable 型別的一個子型別。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
// Some code was removed for brevity.
body: SafeArea(
child: ListenableBuilder(
listenable: viewModel,
builder: (context, _) {
return CustomScrollView(
slivers: [
SliverToBoxAdapter(),
SliverList.builder(
itemCount: viewModel.bookings.length,
itemBuilder: (_, index) =>
_Booking(
key: ValueKey(viewModel.bookings[index].id),
booking: viewModel.bookings[index],
onTap: () =>
context.push(Routes.bookingWithId(
viewModel.bookings[index].id)
),
onDismissed: (_) =>
viewModel.deleteBooking.execute(
viewModel.bookings[index].id,
),
),
),
],
);
}
)
)
);
}處理使用者事件
#最後,View 需要監聽使用者的事件,以便 ViewModel 可以處理這些事件。這透過在 ViewModel 類中公開一個封裝所有邏輯的回撥方法來實現。
在 HomeScreen 中,使用者可以透過滑動 Dismissible 小部件來刪除之前預訂的活動。
回想上一程式碼片段中的程式碼:
SliverList.builder(
itemCount: widget.viewModel.bookings.length,
itemBuilder: (_, index) => _Booking(
key: ValueKey(viewModel.bookings[index].id),
booking: viewModel.bookings[index],
onTap: () => context.push(
Routes.bookingWithId(viewModel.bookings[index].id)
),
onDismissed: (_) =>
viewModel.deleteBooking.execute(widget.viewModel.bookings[index].id),
),
),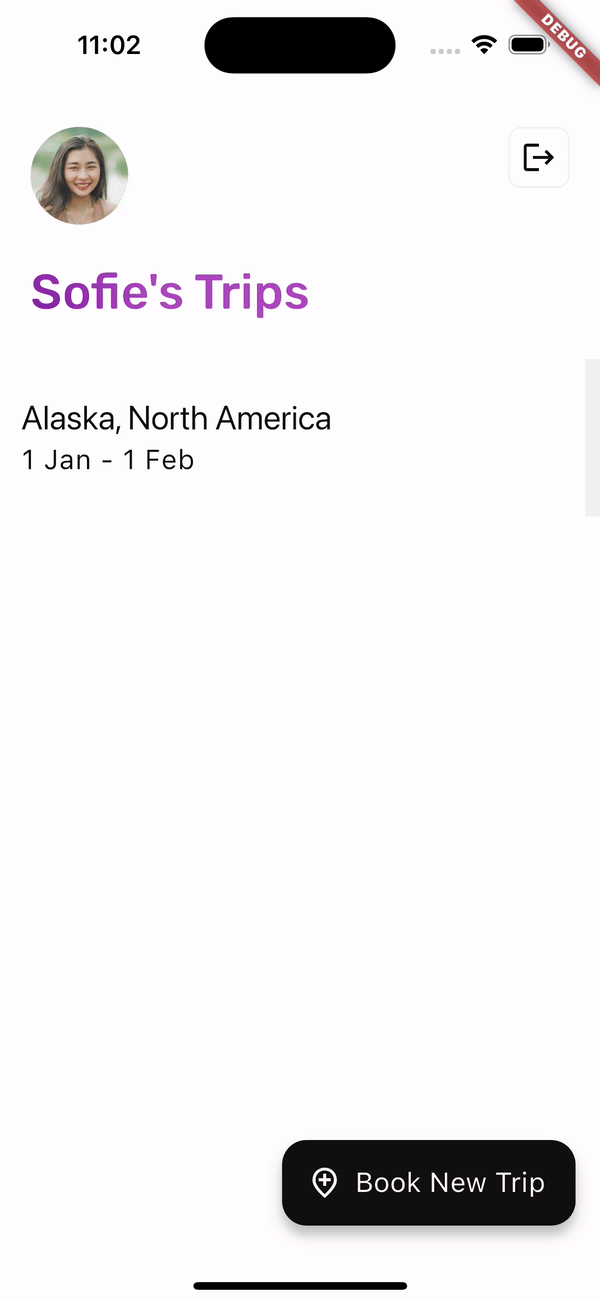
在 HomeScreen 中,使用者的已儲存行程由 _Booking 小部件表示。當 _Booking 被滑動刪除時,將執行 viewModel.deleteBooking 方法。
已儲存的預訂是應用程式狀態,它比會話或 View 的生命週期更持久,只有儲存庫應該修改這種應用程式狀態。因此,HomeViewModel.deleteBooking 方法反過來呼叫資料層中儲存庫公開的一個方法,如以下程式碼片段所示。
Future<Result<void>> _deleteBooking(int id) async {
try {
final resultDelete = await _bookingRepository.delete(id);
switch (resultDelete) {
case Ok<void>():
_log.fine('Deleted booking $id');
case Error<void>():
_log.warning('Failed to delete booking $id', resultDelete.error);
return resultDelete;
}
// Some code was omitted for brevity.
// final resultLoadBookings = ...;
return resultLoadBookings;
} finally {
notifyListeners();
}
}在 Compass 應用中,這些處理使用者事件的方法稱為命令。
Command 物件
#命令負責從 UI 層開始並流向資料層的互動。特別是在此應用中,Command 也是一種型別,它有助於安全地更新 UI,無論響應時間或內容如何。
Command 類包裝了一個方法,並有助於處理該方法的不同狀態,例如 running、complete 和 error。當 Command.running 為 true 時,這些狀態可以輕鬆地顯示不同的 UI,例如載入指示器。
以下是 Command 類的程式碼。出於演示目的,已省略部分程式碼。
abstract class Command<T> extends ChangeNotifier {
Command();
bool running = false;
Result<T>? _result;
/// true if action completed with error
bool get error => _result is Error;
/// true if action completed successfully
bool get completed => _result is Ok;
/// Internal execute implementation
Future<void> _execute(action) async {
if (_running) return;
// Emit running state - e.g. button shows loading state
_running = true;
_result = null;
notifyListeners();
try {
_result = await action();
} finally {
_running = false;
notifyListeners();
}
}
}Command 類本身擴充套件了 ChangeNotifier,在 Command.execute 方法中,會多次呼叫 notifyListeners。這允許 View 以極少的邏輯處理不同的狀態,您將在本頁稍後看到一個示例。
您可能還注意到 Command 是一個抽象類。它由具體的類(如 Command0、Command1)實現。類名中的整數指的是底層方法期望的引數數量。您可以在 Compass 應用的utils 目錄中看到這些實現類的示例。
確保 View 在資料存在前即可渲染
#在 ViewModel 類中,命令是在建構函式中建立的。
class HomeViewModel extends ChangeNotifier {
HomeViewModel({
required BookingRepository bookingRepository,
required UserRepository userRepository,
}) : _bookingRepository = bookingRepository,
_userRepository = userRepository {
// Load required data when this screen is built.
load = Command0(_load)..execute();
deleteBooking = Command1(_deleteBooking);
}
final BookingRepository _bookingRepository;
final UserRepository _userRepository;
late Command0 load;
late Command1<void, int> deleteBooking;
User? _user;
User? get user => _user;
List<BookingSummary> _bookings = [];
List<BookingSummary> get bookings => _bookings;
Future<Result> _load() async {
// ...
}
Future<Result<void>> _deleteBooking(int id) async {
// ...
}
// ...
}Command.execute 方法是非同步的,因此它不能保證在 View 想要渲染時資料可用。這就引出了 Compass 應用使用 Commands 的原因。在 View 的 Widget.build 方法中,該命令用於有條件地渲染不同的 widget。
// ...
child: ListenableBuilder(
listenable: viewModel.load,
builder: (context, child) {
if (viewModel.load.running) {
return const Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
}
if (viewModel.load.error) {
return ErrorIndicator(
title: AppLocalization.of(context).errorWhileLoadingHome,
label: AppLocalization.of(context).tryAgain,
onPressed: viewModel.load.execute,
);
}
// The command has completed without error.
// Return the main view widget.
return child!;
},
),
// ...因為 load 命令是 ViewModel 的一個屬性,而不是短暫的,所以 load 方法何時被呼叫或何時解析並不重要。例如,如果 load 命令在 HomeScreen 小部件建立之前就解析了,這也不是問題,因為 Command 物件仍然存在,並且公開了正確的狀態。
這種模式標準化了應用中常見 UI 問題的解決方案,使您的程式碼庫更不容易出錯且更具可伸縮性,但這並不是每個應用都想實現的模式。是否要使用它在很大程度上取決於您做出的其他架構選擇。許多幫助您管理狀態的庫都有自己的工具來解決這些問題。例如,如果您在應用中使用流和StreamBuilders,Flutter 提供的AsyncSnapshot 類已經內建了此功能。
反饋
#隨著本網站這一部分的不斷發展,我們歡迎您的反饋!