使用操作和快捷方式
本頁介紹如何將物理鍵盤事件繫結到使用者介面中的操作。例如,如果想在應用程式中定義鍵盤快捷方式,本頁就是為你準備的。
概述
#對於 GUI 應用程式來說,要執行任何操作,它都必須有操作:使用者希望告訴應用程式“做”某事。操作通常是直接執行操作的簡單函式(例如設定值或儲存檔案)。然而,在大型應用程式中,事情更為複雜:呼叫操作的程式碼和操作本身的程式碼可能需要放在不同的地方。快捷方式(按鍵繫結)可能需要在完全不知道它們所呼叫的操作的級別上定義。
這就是 Flutter 的操作和快捷方式系統的用武之地。它允許開發者定義實現與其繫結的意圖的操作。在此上下文中,意圖是使用者希望執行的通用操作,而 Intent 類例項在 Flutter 中表示這些使用者意圖。一個 Intent 可以是通用的,在不同的上下文中由不同的操作實現。Action 可以是一個簡單的回撥(如 CallbackAction 的情況),也可以是更復雜的東西,它與整個撤銷/重做架構(例如)或其他邏輯整合。
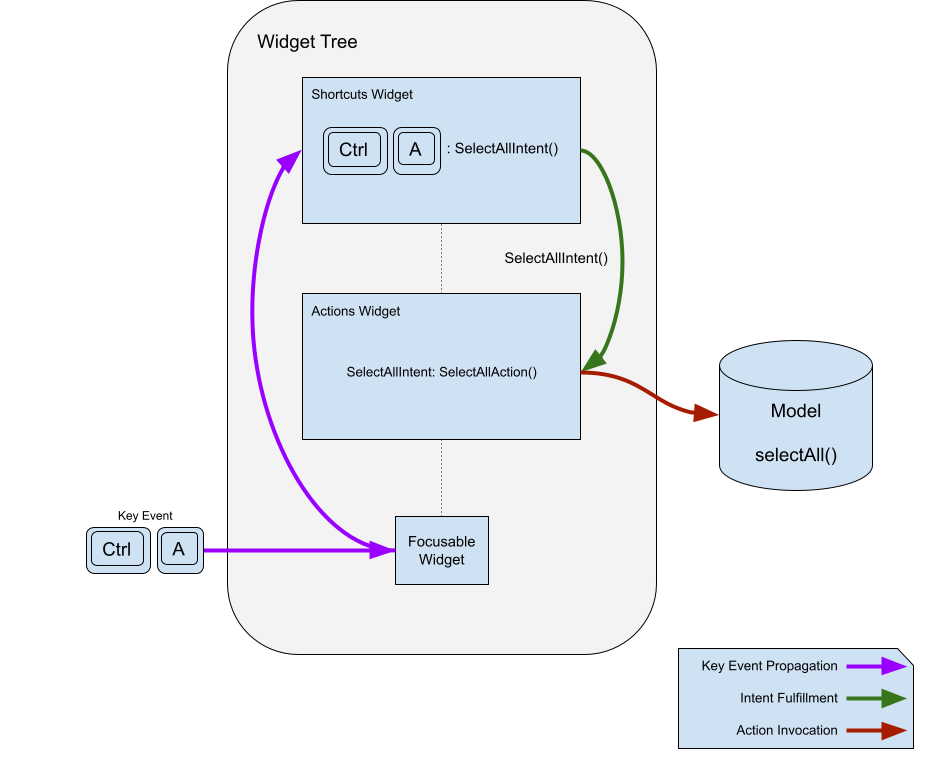
Shortcuts 是透過按下鍵或組合鍵啟用的按鍵繫結。按鍵組合及其繫結的意圖儲存在一個表中。當 Shortcuts 小部件呼叫它們時,它會將匹配的意圖傳送到操作子系統進行實現。
為了說明操作和快捷方式中的概念,本文將建立一個簡單的應用程式,允許使用者使用按鈕和快捷方式在文字欄位中選擇和複製文字。
為什麼要將操作與意圖分離?
#你可能會想:為什麼不直接將按鍵組合對映到操作呢?為什麼還要用意圖呢?這是因為將按鍵對映定義(通常在高級別)與操作定義(通常在低級別)分離是有用的,而且重要的是,能夠將單個按鍵組合對映到應用程式中的預期操作,並讓它自動適應針對所聚焦上下文實現該預期操作的任何操作。
例如,Flutter 有一個 ActivateIntent 小部件,它將每種型別的控制元件對映到其相應的 ActivateAction 版本(並執行啟用控制元件的程式碼)。此程式碼通常需要相當私有的訪問許可權才能完成其工作。如果 Intent 提供的額外間接層不存在,則需要將操作的定義提升到 Shortcuts 小部件的定義例項可以看到它們的位置,導致快捷方式對要呼叫的操作了解得比必要的多,並且擁有或提供它原本不需要的狀態。這允許你的程式碼將兩個關注點分離,使其更加獨立。
意圖配置一個操作,以便同一個操作可以用於多種用途。一個例子是 DirectionalFocusIntent,它接受一個移動焦點的方向,允許 DirectionalFocusAction 知道要移動焦點的方向。但要小心:不要在 Intent 中傳遞適用於 Action 的所有呼叫的狀態:這種狀態應該傳遞給 Action 本身的建構函式,以避免 Intent 需要了解太多。
為什麼不使用回撥?
#你可能還會想:為什麼不直接使用回撥而不是 Action 物件呢?主要原因是,操作透過實現 isEnabled 來決定它們是否啟用是很有用的。此外,如果按鍵繫結和這些繫結的實現位於不同的位置,通常會很有幫助。
如果你只需要回撥,而不需要 Actions 和 Shortcuts 的靈活性,你可以使用 CallbackShortcuts 小部件。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return CallbackShortcuts(
bindings: <ShortcutActivator, VoidCallback>{
const SingleActivator(LogicalKeyboardKey.arrowUp): () {
setState(() => count = count + 1);
},
const SingleActivator(LogicalKeyboardKey.arrowDown): () {
setState(() => count = count - 1);
},
},
child: Focus(
autofocus: true,
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
const Text('Press the up arrow key to add to the counter'),
const Text('Press the down arrow key to subtract from the counter'),
Text('count: $count'),
],
),
),
);
}快捷方式
#正如你將在下面看到的,操作本身很有用,但最常見的用例是將其繫結到鍵盤快捷方式。這就是 Shortcuts 小部件的用途。
它被插入到小部件層次結構中,以定義當按下某個鍵組合時表示使用者意圖的鍵組合。為了將鍵組合的預期目的轉換為具體操作,Actions 小部件用於將 Intent 對映到 Action。例如,你可以定義一個 SelectAllIntent,並將其繫結到你自己的 SelectAllAction 或 CanvasSelectAllAction,透過一個鍵繫結,系統將根據你的應用程式的哪一部分獲得焦點來呼叫其中一個。讓我們看看鍵繫結部分是如何工作的。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Shortcuts(
shortcuts: <LogicalKeySet, Intent>{
LogicalKeySet(LogicalKeyboardKey.control, LogicalKeyboardKey.keyA):
const SelectAllIntent(),
},
child: Actions(
dispatcher: LoggingActionDispatcher(),
actions: <Type, Action<Intent>>{
SelectAllIntent: SelectAllAction(model),
},
child: Builder(
builder: (context) => TextButton(
onPressed: Actions.handler<SelectAllIntent>(
context,
const SelectAllIntent(),
),
child: const Text('SELECT ALL'),
),
),
),
);
}提供給 Shortcuts 小部件的對映將 LogicalKeySet(或 ShortcutActivator,請參見下面的註釋)對映到 Intent 例項。邏輯鍵集定義了一組一個或多個鍵,意圖指示按鍵的預期目的。Shortcuts 小部件在對映中查詢按鍵,以找到一個 Intent 例項,然後將其提供給操作的 invoke() 方法。
ShortcutManager
#快捷方式管理器是一個比 Shortcuts 小部件生命週期更長的物件,它在收到按鍵事件時將其傳遞下去。它包含決定如何處理按鍵的邏輯、遍歷樹以查詢其他快捷方式對映的邏輯,並維護一個按鍵組合到意圖的對映。
雖然 ShortcutManager 的預設行為通常是可取的,但 Shortcuts 小部件接受一個你可以子類化以自定義其功能的 ShortcutManager。
例如,如果你想記錄 Shortcuts 小部件處理的每個按鍵,你可以建立一個 LoggingShortcutManager。
class LoggingShortcutManager extends ShortcutManager {
@override
KeyEventResult handleKeypress(BuildContext context, KeyEvent event) {
final KeyEventResult result = super.handleKeypress(context, event);
if (result == KeyEventResult.handled) {
print('Handled shortcut $event in $context');
}
return result;
}
}現在,每當 Shortcuts 小部件處理一個快捷方式時,它都會打印出按鍵事件和相關上下文。
動作
#Actions 允許定義應用程式可以透過使用 Intent 呼叫它們來執行的操作。操作可以啟用或停用,並接收呼叫它們的意圖例項作為引數,以允許意圖進行配置。
定義操作
#最簡單的操作只是 Action<Intent> 的子類,帶有一個 invoke() 方法。這是一個簡單的操作,它只是在提供的模型上呼叫一個函式。
class SelectAllAction extends Action<SelectAllIntent> {
SelectAllAction(this.model);
final Model model;
@override
void invoke(covariant SelectAllIntent intent) => model.selectAll();
}或者,如果建立新類太麻煩,可以使用 CallbackAction。
CallbackAction(onInvoke: (intent) => model.selectAll());一旦你有了操作,就可以使用 Actions 小部件將其新增到你的應用程式中,該小部件接受一個從 Intent 型別到 Action 的對映。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Actions(
actions: <Type, Action<Intent>>{SelectAllIntent: SelectAllAction(model)},
child: child,
);
}Shortcuts 小部件使用 Focus 小部件的上下文和 Actions.invoke 來查詢要呼叫的操作。如果 Shortcuts 小部件在遇到的第一個 Actions 小部件中沒有找到匹配的意圖型別,它會考慮下一個祖先 Actions 小部件,依此類推,直到它到達小部件樹的根部,或者找到匹配的意圖型別並呼叫相應的操作。
呼叫操作
#作業系統有幾種呼叫操作的方法。迄今為止最常見的方法是使用上一節中介紹的 Shortcuts 小部件,但還有其他方法可以查詢操作子系統並呼叫操作。可以呼叫未繫結到鍵的操作。
例如,要查詢與意圖關聯的操作,你可以使用
Action<SelectAllIntent>? selectAll = Actions.maybeFind<SelectAllIntent>(
context,
);如果給定 context 中存在與 SelectAllIntent 型別關聯的 Action,則此方法返回該 Action。如果不存在,則返回 null。如果關聯的 Action 應該始終存在,則使用 find 而不是 maybeFind,後者在未找到匹配的 Intent 型別時會丟擲異常。
要呼叫操作(如果存在),請呼叫
Object? result;
if (selectAll != null) {
result = Actions.of(
context,
).invokeAction(selectAll, const SelectAllIntent());
}將其合併到一個呼叫中,如下所示:
Object? result = Actions.maybeInvoke<SelectAllIntent>(
context,
const SelectAllIntent(),
);有時,你希望透過按下按鈕或其他控制元件來呼叫操作。你可以使用 Actions.handler 函式來完成此操作。如果意圖對映到啟用的操作,則 Actions.handler 函式會建立一個處理程式閉包。但是,如果沒有對映,則返回 null。這允許在上下文中沒有匹配的啟用操作時停用按鈕。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Actions(
actions: <Type, Action<Intent>>{SelectAllIntent: SelectAllAction(model)},
child: Builder(
builder: (context) => TextButton(
onPressed: Actions.handler<SelectAllIntent>(
context,
SelectAllIntent(controller: controller),
),
child: const Text('SELECT ALL'),
),
),
);
}Actions 小部件僅在 isEnabled(Intent intent) 返回 true 時呼叫操作,這允許操作決定分發器是否應考慮呼叫它。如果操作未啟用,則 Actions 小部件會給小部件層次結構中更高層級的另一個啟用操作(如果存在)執行的機會。
前面的示例使用了 Builder,因為 Actions.handler 和 Actions.invoke(例如)只在提供的 context 中查詢操作,如果示例傳遞了提供給 build 函式的 context,框架將開始在當前小部件“之上”查詢。使用 Builder 允許框架在相同的 build 函式中找到定義的操作。
你可以在不需要 BuildContext 的情況下呼叫操作,但由於 Actions 小部件需要上下文才能找到要呼叫的啟用操作,因此你需要提供一個上下文,可以透過建立自己的 Action 例項,或使用 Actions.find 在適當的上下文中找到一個。
要呼叫操作,請將操作傳遞給 ActionDispatcher 上的 invoke 方法,無論是你自己建立的,還是使用 Actions.of(context) 方法從現有 Actions 小部件檢索的。在呼叫 invoke 之前,請檢查操作是否已啟用。當然,你也可以直接在操作本身上呼叫 invoke,傳入一個 Intent,但這樣你就放棄了操作分發器可能提供的任何服務(例如日誌記錄、撤銷/重做等)。
操作分發器
#大多數時候,你只想呼叫一個操作,讓它完成它的工作,然後就忘了它。但是,有時你可能想記錄已執行的操作。
這就是用自定義分發器替換預設 ActionDispatcher 的地方。你將 ActionDispatcher 傳遞給 Actions 小部件,它會從該小部件下方未設定自己的分發器的任何 Actions 小部件中呼叫操作。
Actions 在呼叫操作時所做的第一件事是查詢 ActionDispatcher 並將操作傳遞給它進行呼叫。如果不存在,它會建立一個預設的 ActionDispatcher,該分發器只會呼叫操作。
但是,如果你想記錄所有被呼叫的操作,你可以建立自己的 LoggingActionDispatcher 來完成這項工作。
class LoggingActionDispatcher extends ActionDispatcher {
@override
Object? invokeAction(
covariant Action<Intent> action,
covariant Intent intent, [
BuildContext? context,
]) {
print('Action invoked: $action($intent) from $context');
super.invokeAction(action, intent, context);
return null;
}
@override
(bool, Object?) invokeActionIfEnabled(
covariant Action<Intent> action,
covariant Intent intent, [
BuildContext? context,
]) {
print('Action invoked: $action($intent) from $context');
return super.invokeActionIfEnabled(action, intent, context);
}
}然後你把它傳遞給你的頂層 Actions 小部件。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Actions(
dispatcher: LoggingActionDispatcher(),
actions: <Type, Action<Intent>>{SelectAllIntent: SelectAllAction(model)},
child: Builder(
builder: (context) => TextButton(
onPressed: Actions.handler<SelectAllIntent>(
context,
const SelectAllIntent(),
),
child: const Text('SELECT ALL'),
),
),
);
}這將在每次執行操作時記錄下來,如下所示:
flutter: Action invoked: SelectAllAction#906fc(SelectAllIntent#a98e3) from Builder(dependencies: _[ActionsMarker])整合起來
#Actions 和 Shortcuts 的組合功能強大:你可以定義通用意圖,這些意圖在小部件級別對映到特定操作。這是一個簡單的應用程式,說明了上述概念。該應用程式建立了一個文字欄位,旁邊還有“全選”和“複製到剪貼簿”按鈕。按鈕呼叫操作來完成其工作。所有呼叫的操作和快捷方式都已記錄。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
/// A text field that also has buttons to select all the text and copy the
/// selected text to the clipboard.
class CopyableTextField extends StatefulWidget {
const CopyableTextField({super.key, required this.title});
final String title;
@override
State<CopyableTextField> createState() => _CopyableTextFieldState();
}
class _CopyableTextFieldState extends State<CopyableTextField> {
late final TextEditingController controller = TextEditingController();
@override
void dispose() {
controller.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Actions(
dispatcher: LoggingActionDispatcher(),
actions: <Type, Action<Intent>>{
ClearIntent: ClearAction(controller),
CopyIntent: CopyAction(controller),
SelectAllIntent: SelectAllAction(controller),
},
child: Builder(
builder: (context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Row(
children: <Widget>[
const Spacer(),
Expanded(child: TextField(controller: controller)),
IconButton(
icon: const Icon(Icons.copy),
onPressed: Actions.handler<CopyIntent>(
context,
const CopyIntent(),
),
),
IconButton(
icon: const Icon(Icons.select_all),
onPressed: Actions.handler<SelectAllIntent>(
context,
const SelectAllIntent(),
),
),
const Spacer(),
],
),
),
);
},
),
);
}
}
/// A ShortcutManager that logs all keys that it handles.
class LoggingShortcutManager extends ShortcutManager {
@override
KeyEventResult handleKeypress(BuildContext context, KeyEvent event) {
final KeyEventResult result = super.handleKeypress(context, event);
if (result == KeyEventResult.handled) {
print('Handled shortcut $event in $context');
}
return result;
}
}
/// An ActionDispatcher that logs all the actions that it invokes.
class LoggingActionDispatcher extends ActionDispatcher {
@override
Object? invokeAction(
covariant Action<Intent> action,
covariant Intent intent, [
BuildContext? context,
]) {
print('Action invoked: $action($intent) from $context');
super.invokeAction(action, intent, context);
return null;
}
}
/// An intent that is bound to ClearAction in order to clear its
/// TextEditingController.
class ClearIntent extends Intent {
const ClearIntent();
}
/// An action that is bound to ClearIntent that clears its
/// TextEditingController.
class ClearAction extends Action<ClearIntent> {
ClearAction(this.controller);
final TextEditingController controller;
@override
Object? invoke(covariant ClearIntent intent) {
controller.clear();
return null;
}
}
/// An intent that is bound to CopyAction to copy from its
/// TextEditingController.
class CopyIntent extends Intent {
const CopyIntent();
}
/// An action that is bound to CopyIntent that copies the text in its
/// TextEditingController to the clipboard.
class CopyAction extends Action<CopyIntent> {
CopyAction(this.controller);
final TextEditingController controller;
@override
Object? invoke(covariant CopyIntent intent) {
final String selectedString = controller.text.substring(
controller.selection.baseOffset,
controller.selection.extentOffset,
);
Clipboard.setData(ClipboardData(text: selectedString));
return null;
}
}
/// An intent that is bound to SelectAllAction to select all the text in its
/// controller.
class SelectAllIntent extends Intent {
const SelectAllIntent();
}
/// An action that is bound to SelectAllAction that selects all text in its
/// TextEditingController.
class SelectAllAction extends Action<SelectAllIntent> {
SelectAllAction(this.controller);
final TextEditingController controller;
@override
Object? invoke(covariant SelectAllIntent intent) {
controller.selection = controller.selection.copyWith(
baseOffset: 0,
extentOffset: controller.text.length,
affinity: controller.selection.affinity,
);
return null;
}
}
/// The top level application class.
///
/// Shortcuts defined here are in effect for the whole app,
/// although different widgets may fulfill them differently.
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
static const String title = 'Shortcuts and Actions Demo';
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: title,
theme: ThemeData(
colorScheme: ColorScheme.fromSeed(seedColor: Colors.deepPurple),
),
home: Shortcuts(
shortcuts: <LogicalKeySet, Intent>{
LogicalKeySet(LogicalKeyboardKey.escape): const ClearIntent(),
LogicalKeySet(LogicalKeyboardKey.control, LogicalKeyboardKey.keyC):
const CopyIntent(),
LogicalKeySet(LogicalKeyboardKey.control, LogicalKeyboardKey.keyA):
const SelectAllIntent(),
},
child: const CopyableTextField(title: title),
),
);
}
}
void main() => runApp(const MyApp());